Growing apples is a rewarding endeavor for many gardeners who appreciate the crisp, juicy goodness of freshly picked fruit.
While it may seem like a straightforward process, many questions may arise, particularly when it comes to the time it takes for these trees to develop and ultimately produce their delectable harvest.

The duration required for apple trees to grow and yield fruit largely depends on the variety and the method of propagation.
For instance, apple trees grown from seedlings can take anywhere from 8-10 years before they start bearing fruit. On the other hand, those grown using grafted rootstocks can begin producing apples in just a few years.
Various factors, such as climate and proper care, also play a significant role in the apple tree’s growth and fruit production, making it essential to choose suitable varieties and optimal growing conditions for a successful harvest.
Related: How Long Does It Take Lemons to Grow: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding apple trees
Apple trees are popular fruit-bearing trees that come in various sizes and varieties. They produce delicious fruit and can be a delightful addition to any garden or orchard. There are four main types of apple trees: standard, dwarf, semi-dwarf, and columnar apple trees.
Standard apple trees are the largest and most traditional type, taking up more space but offering higher yields of apples. On the other hand, dwarf apple trees are small and compact, making them easier to maintain and suitable for smaller gardens.

Semi-dwarf trees are a compromise between the two, offering a medium-sized tree with notable fruit production. Lastly, columnar apple trees are unique as they grow vertically with minimal branching, making them perfect for tight spaces.
When it comes to growing apple trees, it’s essential to understand how long it takes for them to mature and bear fruit. Generally, an apple tree grown from seed will take 6-10 years to reach maturity and reliably produce fruit (source). However, this timeframe can vary depending on the type of apple tree and the growing conditions.
Dwarf apple trees usually take less time to produce fruit compared to standard apple trees. This is because they have been grafted onto a rootstock that allows for faster growth and fruiting. It can take anywhere from 5-10 years for an apple tree to bear fruit, depending on the rootstock and growing conditions (source).
Apple fruit formation peaks when blossoms on mature trees are successfully pollinated. To ensure a bountiful harvest, it’s essential to provide your tree with proper care and maintenance.
Soil requirements play a crucial role in the success of growing apple trees. Ideally, apples need a pH range between 6.0-7.0 (source). Enriching the soil with peat moss, compost, and bonemeal before planting helps establish a healthy foundation for your tree.
In summary, understanding the different types of apple trees and their growth habits is essential for successful cultivation. While it may take several years for an apple tree to mature and produce fruit, the rewards are worth the wait and effort. Choose the right variety and provide proper care, and your apple tree will thrive for years to come.
Selecting the right variety
When it comes to growing apples, choosing the right variety is crucial for a successful harvest. There are numerous apple varieties, each with its own unique characteristics, flavor profiles, and growing requirements. Some popular varieties include Honeycrisp, Fuji, Liberty, McIntosh, Golden Delicious, Granny Smith, Arkansas Black, and Cortland.
Honeycrisp apples are known for their crisp texture and sweet taste, making them ideal for eating fresh. Fuji apples are also sweet with a firm texture, and they store well. Liberty apples are an excellent choice for organic gardeners, as they are highly resistant to common apple diseases and pests.
McIntosh apples are versatile and often used for cooking, baking, and juicing. Golden Delicious apples have a sweet flavor and thin skin, making them perfect for eating fresh or using in salads. Granny Smith apples are tart and firm, commonly used in pies and baking recipes.

Arkansas Black apples are known for their dark red, almost black skin. They have a crisp texture and a mild, sweet flavor. Cortland apples are another versatile option for fresh eating, cooking, and baking, and they have a good balance of sweetness and tartness.
In addition to these popular varieties, it’s essential to consider disease-resistant options when choosing which apple trees to plant. Disease-resistant apple tree varieties can reduce the need for chemical treatments and save you time and effort in maintaining your trees. Some examples of disease-resistant apple varieties include Liberty, McIntosh, and Arkansas Black.
To ensure a bountiful harvest, make sure to select apple varieties that are suitable for your climate and local growing conditions. Choosing the right variety for your specific needs will ensure a healthy, productive apple tree that provides you with delicious fruits for years to come.
The planting process
To grow apples successfully, it is important to follow the appropriate steps in the planting process. Begin by selecting a suitable planting site, which should have access to full sun for at least 8 hours per day during the growing season. The soil should be well-drained, fertile, and loamy.
It is recommended to plant grafted apple trees rather than grow them from seed. Grafted trees are typically obtained from a nursery, ensuring that the desired apple variety is produced.
Growing apples from seeds may result in unpredictable fruit quality and size. Grafting involves attaching a scion, which is a cutting from the desired variety to a compatible rootstock. The rootstock determines the final tree’s size and influences factors such as disease resistance and cold tolerance.

When purchasing a grafted apple tree from a nursery, ensure its rootstock is suitable for your specific growing conditions. The rootstock should ideally be disease-resistant and compatible with the soil and climatic conditions in your area.
Spacing is an important consideration when planting apple trees. The distance between trees depends on the rootstock used and the desired tree size.
In general, seedlings or dwarf rootstocks require 8-10 feet of spacing, while semi-dwarf rootstocks need 12-16 feet. Standard rootstocks demand wider spacing, typically around 18-25 feet apart.
During the planting process, dig a hole large enough to accommodate the root system of your grafted apple tree. Place the tree in the hole, making sure the graft union is at least 2-3 inches above the soil line. Backfill the hole with soil, firm it down, and water the tree thoroughly to settle the soil around the roots.
By following these planting guidelines, you can confidently establish apple trees in your garden, providing them with a solid foundation for future growth and abundant fruit production.
Caring for apple trees
Caring for apple trees is essential to ensure a healthy and bountiful harvest of delicious fruits. Proper care mainly involves watering, mulching, pruning, and maintaining ideal growing conditions.
When it comes to watering apple trees, it is important to provide consistent moisture. Water the trees deeply and regularly, especially during dry periods.

The best time to water is in the early morning, allowing the water to penetrate deeply into the roots. To retain moisture and suppress weeds, apply a layer of mulch around the base of the tree, taking care to keep it away from the trunk to avoid rot.
Pruning is an essential part of apple tree maintenance. It helps to shape the tree, promote healthy growth, and ultimately increase fruit production.
It is advised to prune apple trees during their dormant period, which is in late winter or early spring. Remove any dead, damaged, or diseased branches and open up the tree’s canopy to allow sunlight and air to reach the remaining branches.
Feeding apple trees with the right nutrients also plays a significant role in their growth and fruit production. Incorporate compost or aged manure into the soil before planting.
During the growing season, apply a balanced fertilizer to support growth and fruiting. Be sure to follow the package instructions for proper application rates and timings.
Apple trees are generally cold-hardy, but they can be sensitive to extreme temperature fluctuations. The ideal growing environment should provide sufficient humidity, well-draining soil, and appropriate sunlight. As the tree grows, it may reach up to 30 feet tall and will require ample space to accommodate its size.
In conclusion, providing proper care for your apple trees ensures their overall health and increases the likelihood of a successful harvest. By following these guidelines for watering, mulching, pruning, and maintaining the ideal growing conditions, you’ll be well-prepared to enjoy the fruits of your labor.
Understanding pollination
Pollination is an essential process for successful apple growth, as it allows the transfer of pollen grains from the male parts to the female parts of the flower, eventually leading to fruit development.
Most apple trees (Malus x domestica) require cross-pollination, meaning that they depend on pollen from a different apple variety to fertilize their flowers and set fruit. This is where pollinators, such as bees, play a crucial role in transferring pollen between the flowers of different apple varieties.
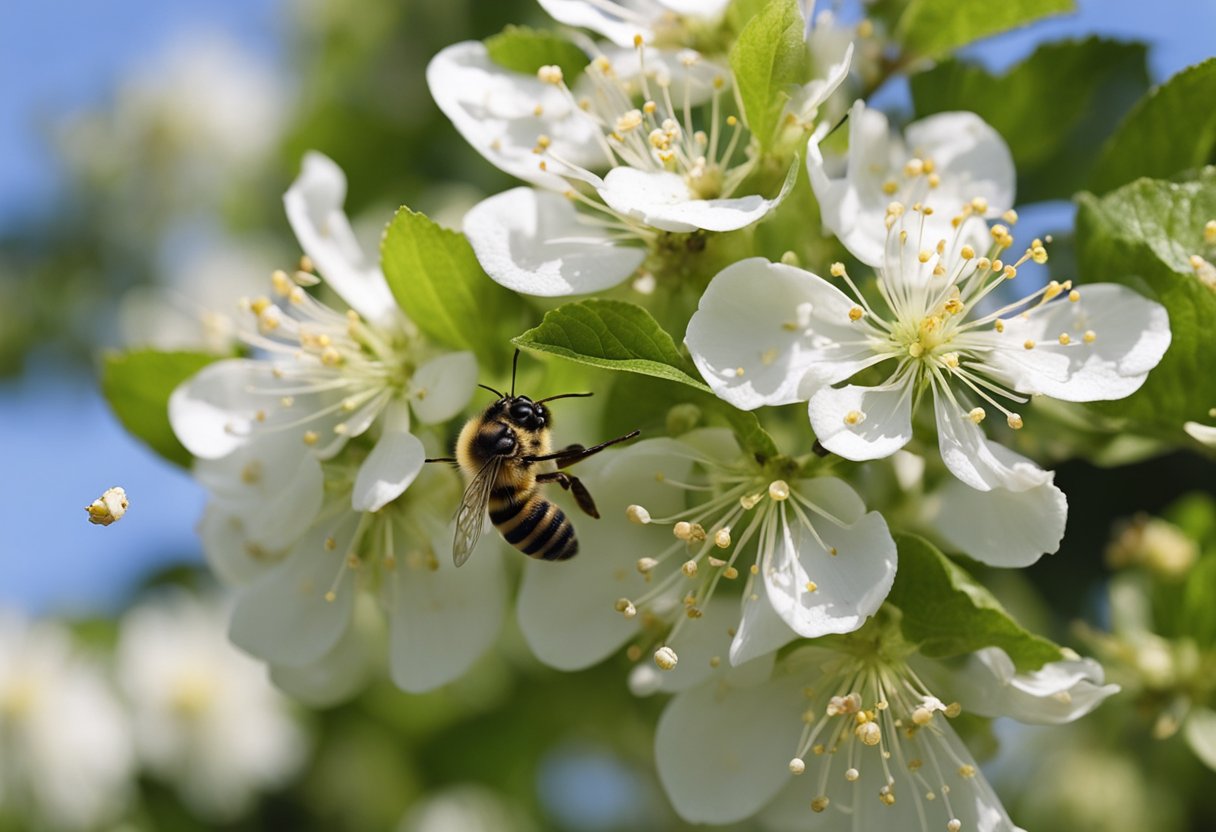

There are a few exceptions with self-pollinating apple trees, which can produce fruit without the need for cross-pollination. However, even self-pollinating varieties can benefit from cross-pollination, as this often leads to better fruit production and quality.
The blooming period is a vital aspect of apple tree pollination. In general, the average blossoming period for apples when pollination can take place is about 9 days.
During this time, flowers are receptive to pollen, and the success of pollination highly depends on the right combination of weather conditions and pollinator activity. Cool weather during bloom will extend this period, whereas warmer weather will shorten it.
Different kinds of apple trees have different bloom periods, usually described as early season, early mid-season, mid-season, mid-late season, and late season. It is important to select apple tree varieties with overlapping bloom times to ensure adequate cross-pollination and fruit production.
In summary, understanding the pollination process and requirements of apple trees is crucial for successful fruit growth. By selecting compatible varieties with overlapping bloom periods and ensuring a healthy pollinator population, gardeners can optimize the pollination process and enjoy a bountiful apple harvest.
Harvesting and storing apples
Harvesting apples is an important process that ensures a high-quality yield. To determine when the apples are ready for harvest, factors such as color, taste, and firmness should be taken into consideration.
Generally, apples develop a transition from tart to sweet flavor as they ripen. It is essential to pick apples at the right time, as they will not ripen further after being picked.
When harvesting apples, take care to avoid damaging the fruit or breaking the fruiting spurs. These spurs are short, compressed stems that produce flowers annually and are essential for future apple production.
For best results, gently twist the apple and lift it away from the tree, ensuring that the stem remains attached to the fruit. This helps in keeping the apples fresh for longer periods during storage.
Storing apples properly is crucial to maintaining their quality. Apples should be stored in a cool, dry place with good ventilation.

Ideal storage conditions include temperatures between 30°F and 32°F with 90% humidity. While storing, sort apples based on their size and condition. This allows for better management of the fruit and prevents spoilage.
It is also essential to thin out the apples on the tree during the growing season. Thinning helps improve the size, color, and overall quality of the fruit, as well as promote better yield in future harvests. To thin apples, remove smaller and damaged fruits, allowing the remaining apples to grow larger and improving air circulation around them.
In summary, carefully harvesting and storing apples is vital for obtaining a high-quality yield. Use knowledge of the apple’s ripeness, gentle handling, and proper storage techniques to ensure the best results. Furthermore, taking steps like thinning during the growing season can improve the overall yield and quality of the apples.
Dealing with pests and diseases
Growing apples can be a rewarding process, but it also comes with its share of challenges. One of the most common issues faced by apple growers is dealing with pests and diseases. A proper pest control strategy is essential in ensuring a healthy and bountiful harvest.
Aphids are one of the most common pests that can be found on apple trees. These small insects feed on the sap, causing the leaves to curl and become discolored.
To effectively control aphids, it is recommended to release beneficial insects such as ladybugs and lacewings that naturally prey on them. Alternatively, you can use a neem oil spray to deter the pests without causing harm to the tree or the environment.
Apple scab is a fungal disease that affects the leaves and fruit, causing dark, scab-like lesions. To prevent apple scab, it is crucial to practice good sanitation by removing fallen leaves and fruit, as they can harbor the fungus. Applying fungicides during the growing season can also help keep the disease under control.
Mites are another common pest that can cause damage to apple trees. Spraying the tree with a horticultural oil can effectively suffocate the mites without harming beneficial insects. Regular monitoring of mite populations is important to catch infestations early and prevent any serious damage to the tree.
Fencing can be an effective method of keeping larger pests like rabbits and deer away from apple trees. By surrounding the trees with a sturdy fence, you can prevent these animals from nibbling on the bark and causing long-term damage to the trees.
When dealing with apple maggots and codling moths, trapping and monitoring are essential for effective pest control. Apple maggot traps, usually red spheres coated with a sticky substance, can be hung in the tree to catch the adult flies. For codling moths, pheromone traps can be placed around the orchard to monitor their presence and determine the best time to apply insecticides.
In some cases, the application of pesticides might be necessary to protect the apple trees from severe infestations or diseases. It is important to select pesticides that specifically target the pests and diseases you are dealing with and follow the label instructions carefully. Always opt for environmentally friendly options whenever possible, and avoid over-spraying to minimize the impact on beneficial insects and the surrounding ecosystem.
By closely monitoring the apple trees for signs of pests and diseases, and taking appropriate action when necessary, apple growers can effectively deal with these challenges and enjoy a healthy, productive harvest.
Using your apples
Once your apple trees have started producing fruit, there are numerous ways to enjoy the harvest. Apples are extremely versatile and can be used in both sweet and savory dishes, as well as consumed in different forms.
Juicing apples is a popular method for making use of the fruit. Fresh apple juice is full of nutrients and can be enjoyed on its own or mixed with other fruit juices for a delicious and healthy beverage.
Some people even prefer making their apple cider by fermenting the juice. This process results in a fizzy, slightly alcoholic drink that can be enjoyed warm or cold, depending on personal preference.
In terms of cooking, apples can be the star ingredient in various recipes. From pies, tarts, and crumbles to sauces and chutneys, the possibilities are endless.

One popular cooking technique is to prepare apple butter, which is a spreadable, spiced apple mixture that is delicious on toast, pancakes, or even mixed into yogurt. Apples can also be added to salads, paired with pork dishes, or used to create an innovative twist on traditional recipes.
When it comes to cider, apples play a crucial role. Cider is made by fermenting apple juice, and it can be either alcoholic or non-alcoholic.
There are countless cider recipes available, allowing one to experiment with different apple varieties, spices, and additional flavors. Cider can also be used in cooking, providing a unique depth of flavor to dishes like pulled pork, glazes, and marinades.
Lastly, consider the placement of your apple trees in your garden. Incorporate them into your existing landscape by planting them as part of a bush or hedge, or even as standalone trees. Apple trees grow best in full sun, so ensure they have at least eight hours of sunlight daily. By doing so, you’ll not only enjoy an abundant apple harvest but also create a visually appealing addition to your outdoor space.